INFORMATION THEFT
breaking into a computer to obtain confidential information. Info can be used or sold for various purposes.Example:stealing a organization´s proprietary info, such as research and development info.
DATA LOSS AND MANIPULATION
breaking into a computer to destroy or alter data records.Examples of date loss:sending a virus that reformats a computer´s hard drive. Examples of data manipulation:breaking into a records system to change information, such as the price of an item.
IDENTITY THEFT
a form of info theft where personal info is stolen for the purpose of taking over someone´s identity. Using this info an individual can obtain legal documents, apply for credit and make unauthorized online purchases.Identity theft is a growing problem costing billions of dollars per year.
DISRUPTION OF SERVICE
preventing legitimate users from accessing services to which they should be entitled.

External Threats
arise from individuals working outside of an organization. They do not have authorized access to the computer systems or network.
Internal threats
occur when someone has authorized access to the network through a user account or have physical access to the network equipment.
SOCIAL ENGINEERING
Techniques uesd by an attacker to manipulate ussuspecting people into providing info or computer system access.
techiniques:
PRETEXTING
fraudulent acquisition of sensitive info, primarily over the telephone, where an invented scenario persuades a target of legitimacy.
PHISHING
fraudulent acquisition os sensitive info through the impersonation of a trustworthy source.
VISHING
fraudulent aquisition of sensitive info through VoIP that terminates in a computer.
VIRUSes
It needs to be activated. Once activated, a virus may do nothing more than replicate itself and spread.A more serious virus may be programmed to delete or corrupt specific files before spreading. Viruses can be transmitted via email attachments, downloaded files, instant messages or via diskette, CD or USB devices.
Worms
Uses the network to send copies of itself to any connected hosts.Do not necessarily require activation or human intervention.
Trojan Horses
is a non-self replicating program that is written to appear like a legitimate program, when in fact it is an attack tool.It may be relatively harmless or can contain code that can damage the contents of the computer's hard drive.Can also create a back door into a system allowing hackers to gain access.

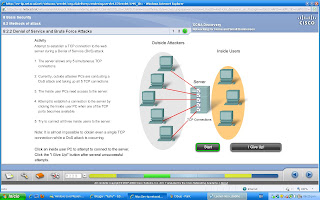
Denial of Service (DoS)
Attacks on an individual computer or groups of computers with the intent to deny services to intended users. DoS attacks can target end user systems, servers, routers, and network links.
In general, DoS attacks seek to:
Flood a system or network with traffic to prevent legitimate network traffic from flowing
Disrupt connections between a client and server to prevent access to a service
Types of Dos attacks:
SYN (synchronous) Flooding: a flood of packets are sent to a server requesting a client connection. The packets contain invalid source IP addresses. The server becomes occupied trying to respond to these fake requests and therefore cannot respond to legitimate ones.
Ping of death: a packet that is greater in size than the maximum allowed by IP (65,535 bytes) is sent to a device. This can cause the receiving system to crash.
DDoS
It is designed to saturate and overwhelm network links with useless data.Operates on a much larger scale than DoS attacks.The attack points may be unsuspecting computers that have been previously infected by the DDoS code.The systems that are infected with the DDoS code attack the target site when invoked.
Brute force attack
Is another type of attack.
A fast computer is used to try to guess passwords or to decipher an encryption code. The attacker tries a large number of possibilities in rapid succession to gain access or crack the code. Brute force attacks can cause a denial of service due to excessive traffic to a specific resource or by locking out user accounts.
SPYWARE
a malicious program, typically installed without a user's knowledge, designed to perform tasks such as capture keystrokes, for the benefit of the originator of the program.
POPUP
a form of online advertising to increase web traffic or capture e-mail addresses that displays when a user opens certain websites or clicks on specific links.
COOKIES
are a form of spyware. They are used to record information about an Internet user when they visit websites.May be useful or desirable by allowing personalization and other time saving techniques. Many web sites require that cookies be enabled in order to allow the user to connect.
ADWARE
is a form of spyware used to collect information about a user based on websites the user visits.Is commonly installed by a user in exchange for a "free" product. When a user opens a browser window, Adware can start new browser instances which attempt to advertize products or services based on a user's surfing practices. The unwanted browser windows can open repeatedly, and can make surfing the Internet very difficult, especially with slow Internet connections.
SPAM
unsolicited or junk e-mail messages sent to multiple recipients for either legitimate or fraudulent purposes.
SECURITY TOOLS
Firewall
controls traffic to and from a network.
Spam filter
software installed on an end-user workstation or server to identify and remove unwanted emails.
Patches and Updates
software applied to an OS or application to correct a known security vulnerability or add functionality.
Anti-spyware
to detect and remove spyware and adware.
Popup blocker
to prevent popups and unders.
Anti-virus
to detect and remove viruses, worms and Trojan.
Some of the signs that a virus, worm or Trojan horse may be present include:
Computer starts acting abnormally
Program does not respond to mouse and keystrokes
Programs starting or shutting down on their own
Email program begins sending out large quantities of email
CPU usage is very high
There are unidentifiable, or a large number of processes running
Computer slows down significantly or crashes
Features that can be included in Anti-virus programs are:
Email checking - Scans incoming and outgoing emails, and identifies suspicious attachments.
Resident dynamic scanning - Checks executable files and documents when they are accessed.
Scheduled scans - Virus scans can be scheduled to run at regular intervals and check specific drives or the entire computer.
Automatic Updates - Checks for, and downloads, known virus characteristics and patterns. Can be scheduled to check for updates on a regular basis.
Actions to prevent the spread of spam include:
Apply OS and application updates when available.
Run an Antivirus program regularly and keep it up to date.
Do not forward suspect emails.
Do not open email attachments, especially from people you do not know.
Set up rules in your email to delete spam that by-pass the anti-spam software.
Identify sources of spam and report it to a network administrator so it can be blocked.
Report incidents to the governmental agency that deals with abuse by spam.
A Firewall is one of the most effective security tools available for protecting internal network users from external threats.Controls the traffic between them as well as helps prevent unauthorized access. Firewall techniques
Packet Filtering - Prevents or allows access based on IP or MAC addresses.
Application Filtering - Prevents or allows access to specific application types based on port numbers.
URL Filtering - Prevents or allows access to websites based on specific URLs or keywords.
Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) - Unsolicited packets are blocked unless permitted specifically. SPI can also include the capability to recognize and filter out specific types of attacks such as DoS.
Firewall products come packaged in various forms:
Appliance-based firewalls -is built-in to a dedicated hardware device known as a security appliance.
Server-based firewalls -consists of a firewall application that runs on a network operating system (NOS) such as UNIX, Windows or Novell.
Integrated Firewalls -implemented by adding firewall functionality to an existing device, such as a router.
Personal firewalls -reside on host computers and are not designed for LAN implementations. They may be available by default from the OS or may be installed from an outside vendor.
USING A FIREWALL


ONE FIREWALL CONFIG
external network
internal network
DMZ.
To monitor the traffic and determine what traffic should be passed to the DMZ,internally, and what should be denied altogether.
TWO FIREWALL CONFIG
There is an internal and external firewall with the DMZ located between them.
A two-firewall configuration is more appropriate for larger, more complex networks that handle a lot more traffic.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario